Program Execution Flow
Program execution process¶
参考 Execution Angleboye@Bamboofox 。
Basic Overview¶
Static execution¶
Here is the basic process of static execution of the program.
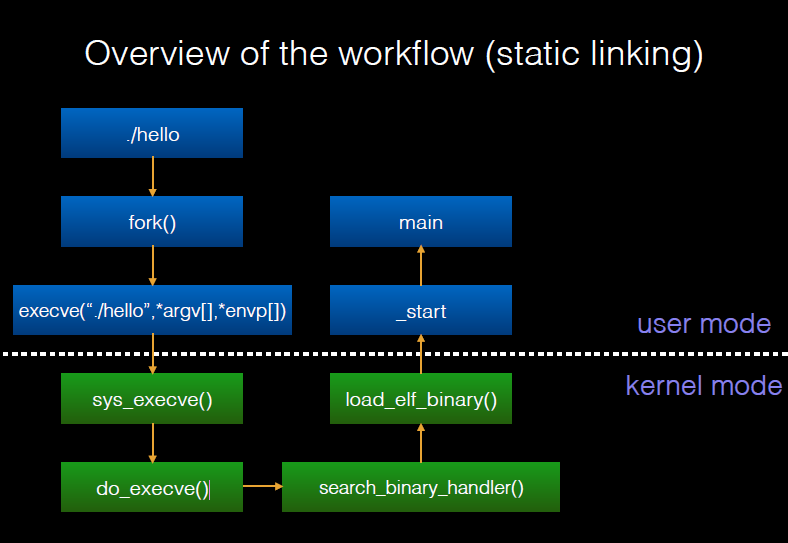
Dynamic execution¶
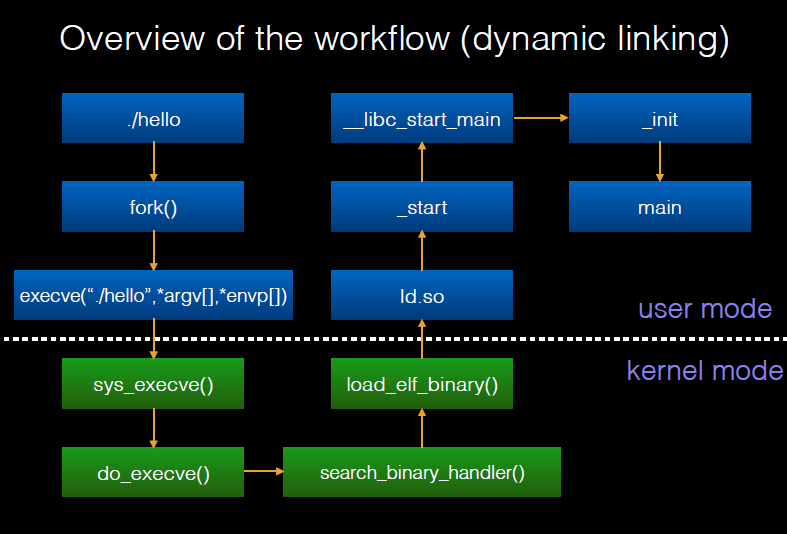
Here is another more detailed picture.
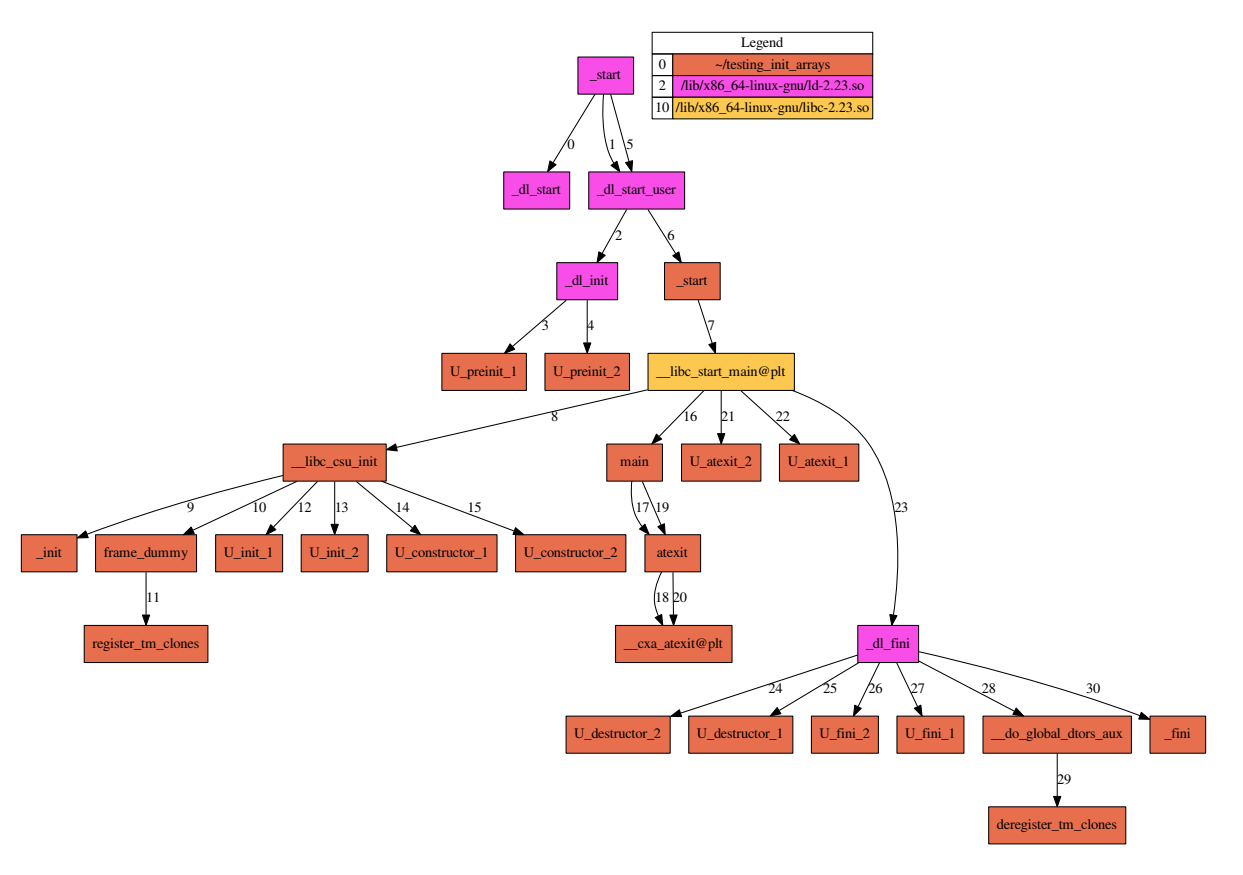
Basic operation instructions¶
sys_execve¶
This function is mainly used to execute a new program, that is, execute the program we want to execute, and check the corresponding parameters such as argv and envp.
do_execve¶
This function opens the target image file and reads the specified length (currently 128 bytes) from the beginning of the target file to get the basic information of the corresponding target file.
search_binary_handler¶
This function searches for a binary type queue that supports handling of the current type, so that the handlers of various executable programs can be processed accordingly.
load_elf_binary¶
The main processing flow of this function is as follows
-
Check and get the header information of the elf file.
-
If the target file is dynamically linked, use the .interp section to determine the path to the loader.
-
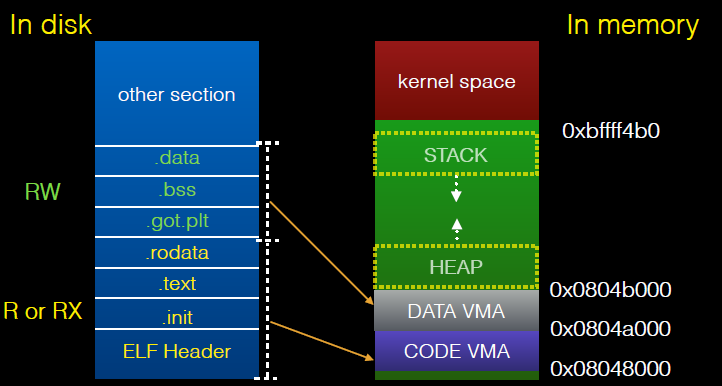
Map the corresponding segments recorded in the program header to memory. The following important information in the program header
-
the address to which each segment needs to be mapped
- The appropriate permissions for each segment.
- Record which sections belong to which sections.
The specific mapping is as follows
Case processing
- In the case of dynamic linking, change the return address of sys_execve to the entry point of loader (ld.so).
- In the case of static linking, change the return address of sys_execve to the entry point of the program.
ld.so¶
This file has the following features
- Mainly used to load shared libraries recorded in DT_NEED in ELF files.
- Initialization work
- Initialize the GOT table.
- Merge the symbol table into the global symbol table.
_start¶
The _start function will hand over the following to libc_start_main
- Environment variable start address
-
.init
-
Initialization before starting the main function
- ends
- Finishing work before the end of the program.
本页面的全部内容在 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 协议之条款下提供,附加条款亦可能应用。