Execute Shellcode¶
Introduction¶
A shellcode is a piece of code that is executed to exploit a software vulnerability. The shellcode is a hexadecimal mechanical code, named after the attacker often gets the shell. Shellcode is often written in machine language. After the scratchpad eip overflows, it inserts a shellcode mechanical code that the CPU can execute, allowing the computer to execute any command from the attacker. The ASLR, NX, and CANARY options are turned off at compile time, so that the shellcode can be placed on the stack at the time of input. The dynamic padding can be used to obtain the required padding overflow to the shellcode address of the input address, so that the shellcode will be executed after the program returns. .
example¶
A classic example is given below. After the program overflows, the shellcode is executed. The compiled environment is vc6.0 for the winxp tool.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#define PASSWORD "1234567"
int verify_password(char *password)
{
int authenticated;
char buffer[50];
authenticated = strcmp(password,PASSWORD);
memcpy(buffer,password,strlen(password));
return authenticated;
}
void main()
{
int valid_flag =0;
char password [1024];
FILE *fp;
LoadLibrary("user32.dll");
if (!(fp=fopen("password.txt","rw+")))
{
exit(0);
}
fscanf(fp,"%s",password);
valid_flag = verify_password(password);
if (valid_flag !=0)
{
printf("incorrect password!\n\n");
}
else
{
printf("Congratulation! You have passed the verification!\n");
}
fclose(fp);
getchar();
}
After compiling, drag into OllyDbg dynamic debugging to determine the length of padding, and the next breakpoint at memcpy for subsequent debugging. You can make a 50 BYTES padding comparison distance from the return address, and finally determine the return address after 60 BYTES.
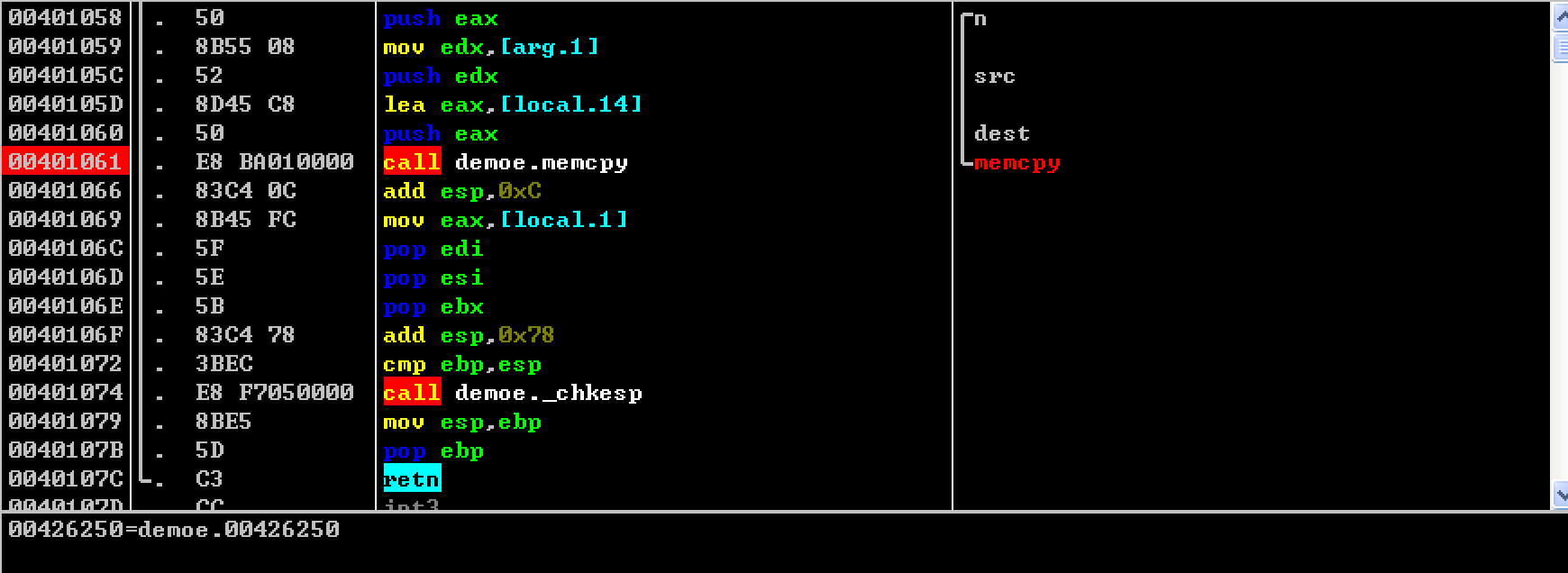
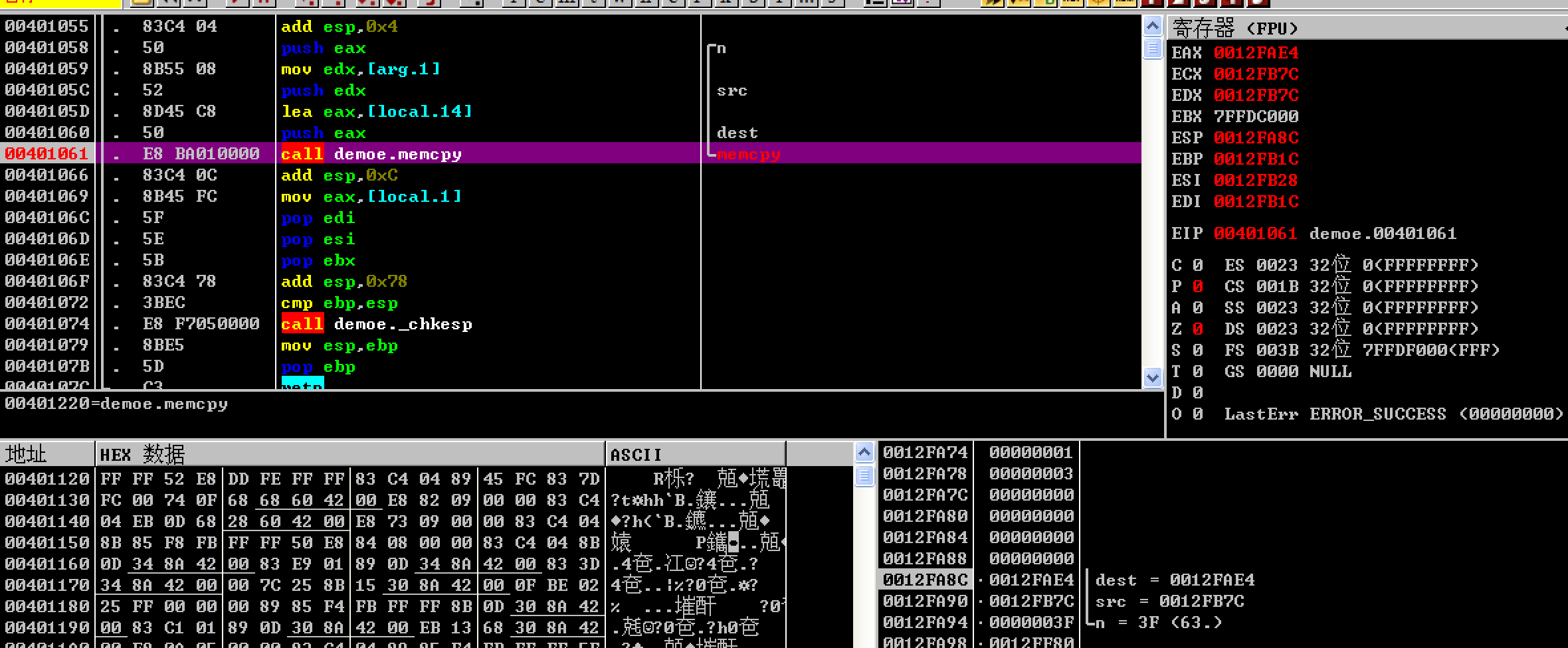
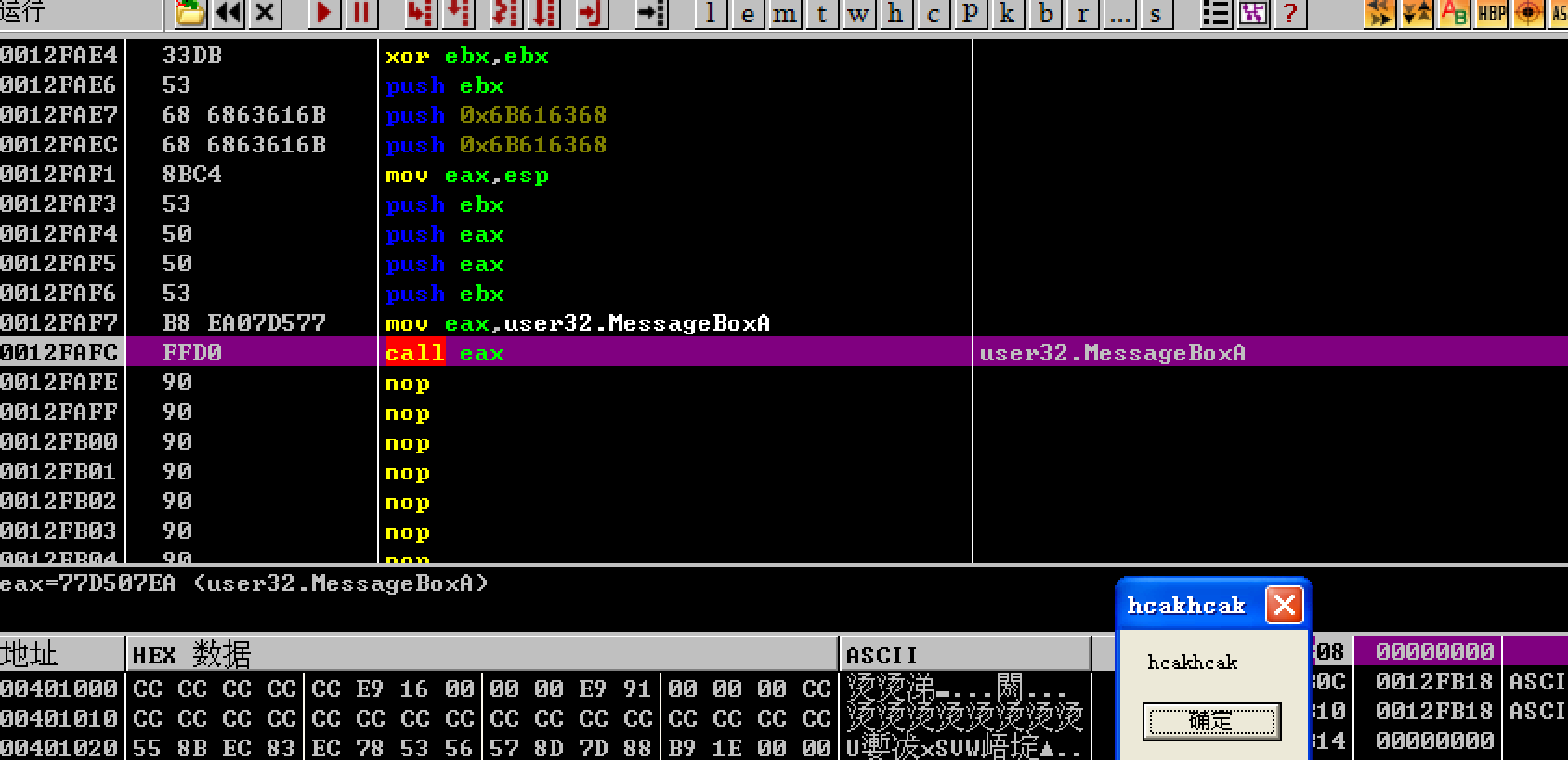
The entered string will be copied to the location of the 0012FAE4 on the stack.
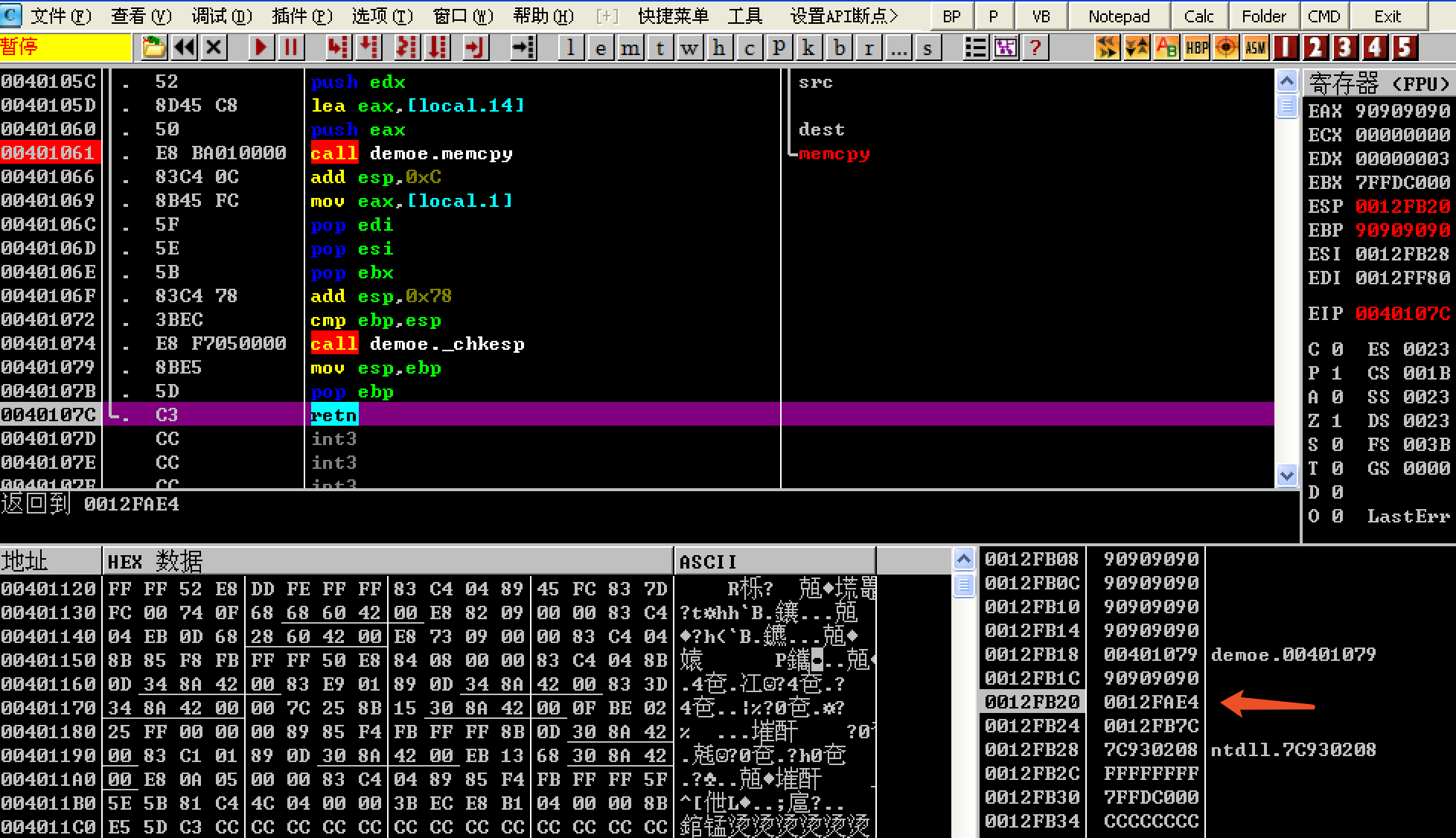
Because the return address is controlled to 0012FAE4 by reasonable padding, the value of the register EIP is 0012FAE4 when the function returns. At this time, the system considers the data in the stack as machine code, the program. The code with the address 0012FAE4 will be executed.
The content in password.txt is a well-arranged machine code. The function is to pop up a message box with hackhack. How to write the contents of password.txt, we will focus on the entire implementation process in the following chapters.
As expected, the pop-up function was performed after the program returned.
Reference reading¶
[0day security: software vulnerability analysis technology] ()
本页面的全部内容在 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 协议之条款下提供,附加条款亦可能应用。