JPG
File Structure¶
-
JPEG has a lossy compression format, the pixel information is saved into a file and then read out, some of the pixel values will have a little change. There is a quality parameter that can be set between 0 and 100 when saving. The larger the parameter, the more fidelity the picture has. In general, 70 or 80 is sufficient
-
JPEG has no transparency information
There are two basic types of JPG data structures: "segments" and compressed encoded image data.
| Name | Number of Bytes | Byte Data | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segment Identification | 1 | FF | Start ID of each new segment |
| Segment Type | 1 | Type Encoding (called Marker) | |
| Segment Length | 2 | Length of content and segment, excluding segment ID and type | |
| Segment Content | 2 | ≤65533 bytes |
- Some segment contains no length or content, but just the segment marking and type. File head and end are examples of this.
- Any amount of
FFbetween segments is valid; theseFF's are called "padding bytes" and must be ignored.
Some common segment types:
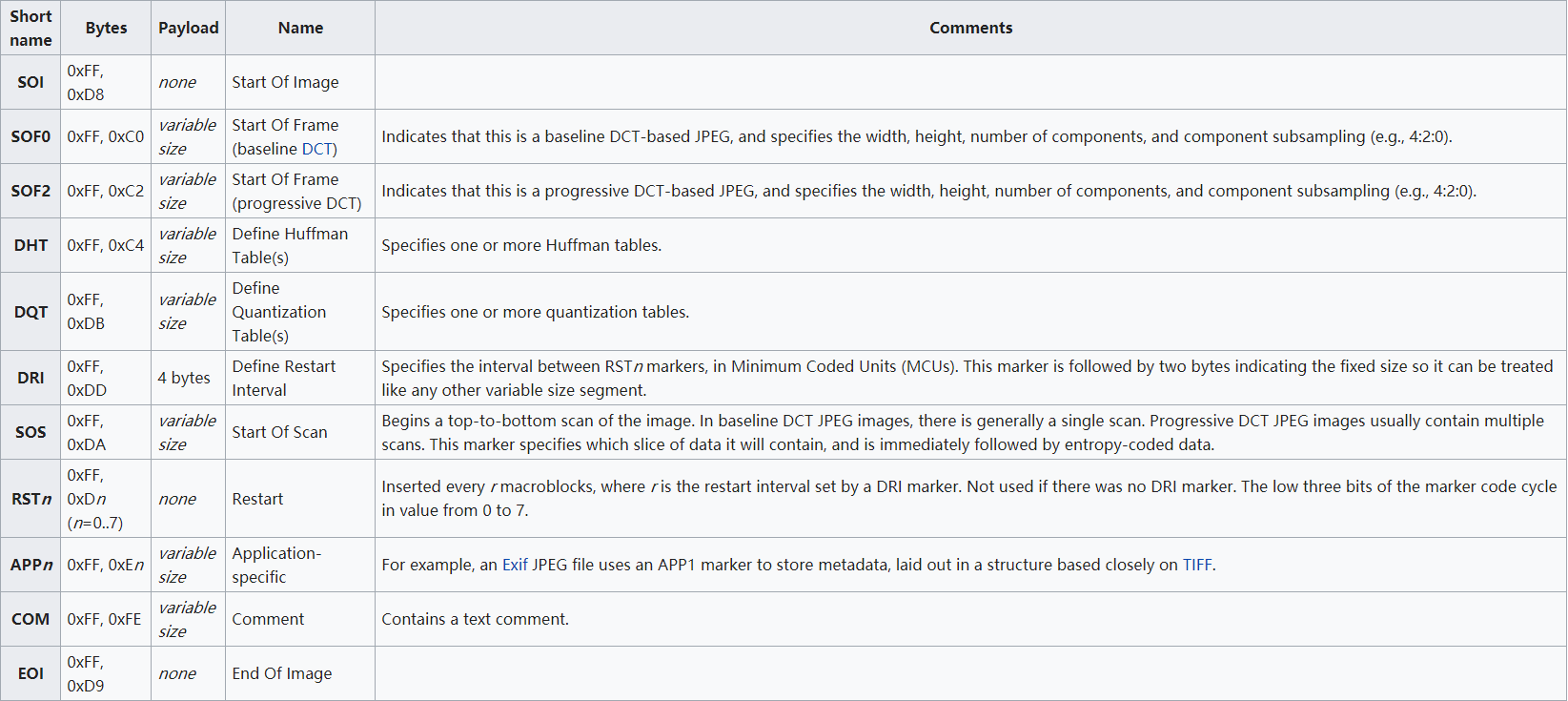
Note that a JPG file starts with 0xffd8 and ends with 0xffd9.
Tools¶
Stegdetect¶
Stegdetect is a tool to detect steganography in image files, it supports different methods, which are used to hide content. Currently, the detectable schemes are: jsteg, jphide, invisible secrets, outguess, F5 (header analysis), appendX and camouflage.
Additionally, it can also brute force passwords and extract information from Jphide, outguess, and jsteg-shell.
-q Only reports images that are likely to have steganographic content.
-n -n Enables checking of JPEG header information to surpress false positives. If enabled, all JPEG images that contain comment fields will be treated as negatives. OutGuess checking will be disabled if the JFIF marker does not match version 1.1.
-s Changes the sensitivity of the detection algorithms. Their results are multiplied by the specified number. The higher the number the more sensitive the test will become. The default is 1.
-d Prints debug information.
-t Sets the tests that are being run on the image. The following characters are understood:
j Tests if information has been embedded with jsteg.
o Tests if information has been embedded with outguess.
p Tests if information has been embedded with jphide.
i Tests if information has been hidden with invisible secrets.
JPHS¶
JPHS is a steganography tool. It is developed by Allan Latham that encrypt, hide, and detect information of lossy compressed JPEG files. The tool contains two programs: JPHIDE and JPSEEK. Jphide program can hide information in a JPEG image. The JPSEEK program can detect and extract information hidden using the JPHIDE program. The JPHSWIN program is a Windows version of JPHS that has a graphical interface that contains JPHIDE and JPSEEK functions.
SilentEye¶
SilentEye is a cross-platform application design for an easy use of steganography, in this case hiding messages into pictures or sounds. It provides a pretty nice interface and an easy integration of new steganography algorithm and cryptography process by using a plug-ins system.
本页面的全部内容在 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 协议之条款下提供,附加条款亦可能应用。